Ttl To Vga Converter
Archives Analog Devices. Newsletters. Interested in the latest news and articles about ADI products, design tools, training and events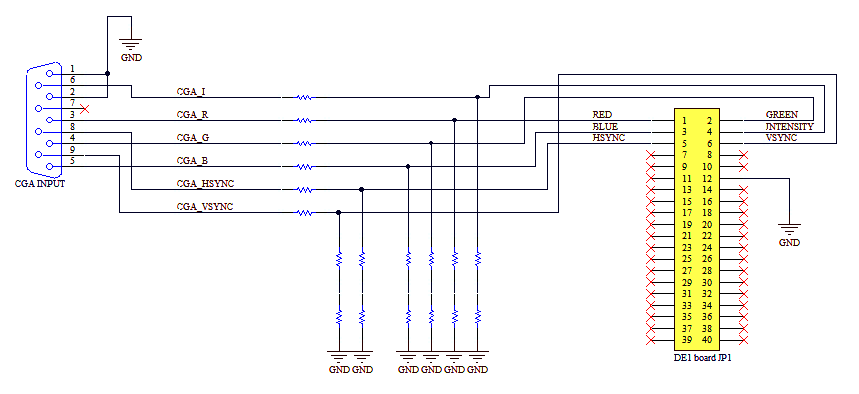 Choose from one of our 1. Ttl To Vga Converter' title='Ttl To Vga Converter' />Color Graphics Adapter Wikipedia. Color Graphics Adapter. Release date. 19. Architecture. Motorola MC6. ATI CW1. 68. 00. Cards. Entry level. IBM Color Graphics Adapter, ATi Graphics Solution Rev 3, ATi Color Emulation Card, Tseng Labs Color. PAK,Mid range. ATi Graphics Solution plus, ATi Graphics Solution Plus SP, ATi Graphics Solution SR, Number Nine Graphics System. High end. ATi Small Wonder Graphics Solution, Tseng Labs EVA4. Enthusiast. ATi Small Wonder Graphics Solution with game port. USB to dual serial port converter with DB9 connectors. RS422RS485 from 99. VGA VideoAudio Splitter Use one computer to display the same highresolution image on numerous monitors up to 256. Also known as VGA splitter, video splitter, VGA. History. Successor. Plantronics Colorplus. PCjrTandy Graphics Adapter. Enhanced Graphics Adapter. Multi Color Graphics Array. Professional Graphics Controller. Original IBM Color Graphics Adapter. The Color Graphics Adapter CGA, originally also called the ColorGraphics Adapter or IBM ColorGraphics Monitor Adapter,1 introduced in 1. IBMs first graphics card and first color display card for the IBM PC. For this reason, it also became that computers first color computer display standard. The standard IBM CGA graphics card was equipped with 1. CRT monitor using a 4 bit digital TTL RGBI interface, such as the IBM 5. NTSC compatible television or composite videomonitor via an RCA connector. The RCA connector provided only baseband video, so to connect the CGA card to a standard television set required a separate RF modulator unless the TV had an RCA jack though with the former combined with an amplifier sometimes was more practical since one could then hook up an antenna to the amplifier and get wireless video. Built around the Motorola MC6. CGA card featured several graphics and text modes. The highest display resolution of any mode was 6. Output capabilitieseditCGA supports 3. Pixel aspect ratio of 1 1. Pixel aspect ratio of 1 2. The pixel aspect ratio stems from rendering said distribution of pixels on a screen with 4 3 proportions, typical of monitors at the time. Text modes 4. Extended graphics modes 1. Artifact colors using a NTSC monitor 1. IBM intended that CGA be compatible with a home television set. The 4. 02. 5 text and 3. Cga p. 0. png CGA 3. Cga p. 1. png CGA 3. Cga p. 3. png CGA 3. CGA program interface. PCPaint in 3. 202. Note the use of dithering to overcome the CGA palette limitations. CGA 6. 40x. 20. 0 game. Sim. City in 6. 402. Note the use of dithering to simulate gray tones and non square pixel ratio that deforms the fonts. Color paletteeditDespite varying bit depths among the CGA graphics modes see below, CGA processes colors in its palette in four bits, yielding 2. The four color bits are arranged according to the RGBI color model the lower three bits represent red, green, and blue color components a fourth intensifier bit, when set, increases the brightness of all three color components red, green, and blue. Employee Compensation Act 1923 Bare Act Pdf. In graphics modes, colors are set per pixel in text modes, colors are set per character, with an independent foreground and background color for each character. Full CGA 1. 6 color palette. AA9light blue5. 55. FF2green0. 0AA0. FF5. AAAA1. FFFF4redAA0. FF5. 55. 55magentaAA0. AA1. 3light magentaFF5. FF6brownAA5. 50. FFFF5. AAAAAA1. FFFFFFWith an RGBI monitoreditThese four bits are passed on unmodified to the DE 9 connector at the back of the card, leaving all color processing to the RGBI monitor connected to it. With respect to the RGBI color model described above, the monitor would use approximately the following formula to process the digital four bit color number to analog voltages ranging from 0. Number 44 13color. Number 88. Number 22 13color. Number 88. Number 11 13color. Number 88. Color 6 is treated differently when using the formula above, color 6 would become dark yellow, as seen to the left, but in order to achieve a more pleasing brown tone, special circuitry in most RGBI monitors, including the IBM 5. Number 6 thengreen green 2. It is this RGBI with tweaked brown palette, shown in the complete palette to the right, that all later PC graphics standards such as EGA and VGA have retained for compatibility as a power on default setting of their internal palette registers andor DAC registers. With a composite color monitortelevision seteditFor the composite output, these four bit color numbers are encoded by the CGAs onboard hardware into an NTSC compatible signal fed to the cards RCA output jack. For cost reasons, this is not done using an RGB to YIQ converter as called for by the NTSC standard, but by a series of flip flops and delay lines. Consequently, the hues seen are lacking in purity notably, both cyan and yellow have a greenish tint, and color 6 again looks dark yellow instead of brown. The relative luminances of the colors produced by the composite color generating circuit differ between CGA revisions they are identical for colors 1 6 and 9 1. CGAs produced until 1. CGAs due to the addition of additional resistors. CGAs 1. 6 colors when using the NTSC output post 1. RGBI monitor availabilityeditWhen the CGA was introduced in 1. IBM did not offer an RGBI monitor. Instead, customers were supposed to use the RCA output with an RF modulator that they obtained separately, from a third party to connect the CGA to their television set. The IBM 5. 15. 3 Personal Computer Color Display would not be introduced until March 1. Resulting from the lack of available RGBI monitors in 1. RGB monitors without provisions for the intensifier bit, reducing the number of available colors to eight, and displaying both colors 6 and 1. This is relevant insofar as if an application or game programmer used either one of these configurations, they will have expected color 6 to look dark yellow instead of brown. Standard text modeseditCGA offers four BIOS text modes called alphanumeric modes in IBMs documentation 4. Each character is a pattern of 88 dots. The effective screen resolution in this mode is 3. The choice of patterns for any location is thus limited to one of the 2. ROM chip on the card itself. The display font in text mode the hardware code page. IBM CGA, it is possible to select one of two different fontsnormal or thinby changing a jumper. Many clones didnt offer this possibility. The card has sufficient video RAM for eight different text pages in this mode. BIOS Modes 0 1 select 4. The difference between these two modes can only be seen on a composite monitor mode 0 disables the color burst, making colors appear in grayscale. Mode 1 enables the color burst, allowing for color. Mode 0 and Mode 1 are functionally identical on RGB monitors and on later adapters that emulate CGA without supporting composite color output. Each character is again an 88 dot pattern the same character set is used as for 4. The effective screen resolution of this mode is 6. Again, the pixels cannot be individually addressed. Since there are twice as many characters on the screen in this mode, the card has enough video RAM for just four different text pages. BIOS Modes 2 3 select 8. As with the 4. 0 column text modes, Mode 2 disables the color burst in the composite signal and Mode 3 enables it. In every text mode, each character has a background and a foreground colore. While the same 4 bit nybble value used for the foreground color would normally allow all 1. CGA independent of the CPU.
Choose from one of our 1. Ttl To Vga Converter' title='Ttl To Vga Converter' />Color Graphics Adapter Wikipedia. Color Graphics Adapter. Release date. 19. Architecture. Motorola MC6. ATI CW1. 68. 00. Cards. Entry level. IBM Color Graphics Adapter, ATi Graphics Solution Rev 3, ATi Color Emulation Card, Tseng Labs Color. PAK,Mid range. ATi Graphics Solution plus, ATi Graphics Solution Plus SP, ATi Graphics Solution SR, Number Nine Graphics System. High end. ATi Small Wonder Graphics Solution, Tseng Labs EVA4. Enthusiast. ATi Small Wonder Graphics Solution with game port. USB to dual serial port converter with DB9 connectors. RS422RS485 from 99. VGA VideoAudio Splitter Use one computer to display the same highresolution image on numerous monitors up to 256. Also known as VGA splitter, video splitter, VGA. History. Successor. Plantronics Colorplus. PCjrTandy Graphics Adapter. Enhanced Graphics Adapter. Multi Color Graphics Array. Professional Graphics Controller. Original IBM Color Graphics Adapter. The Color Graphics Adapter CGA, originally also called the ColorGraphics Adapter or IBM ColorGraphics Monitor Adapter,1 introduced in 1. IBMs first graphics card and first color display card for the IBM PC. For this reason, it also became that computers first color computer display standard. The standard IBM CGA graphics card was equipped with 1. CRT monitor using a 4 bit digital TTL RGBI interface, such as the IBM 5. NTSC compatible television or composite videomonitor via an RCA connector. The RCA connector provided only baseband video, so to connect the CGA card to a standard television set required a separate RF modulator unless the TV had an RCA jack though with the former combined with an amplifier sometimes was more practical since one could then hook up an antenna to the amplifier and get wireless video. Built around the Motorola MC6. CGA card featured several graphics and text modes. The highest display resolution of any mode was 6. Output capabilitieseditCGA supports 3. Pixel aspect ratio of 1 1. Pixel aspect ratio of 1 2. The pixel aspect ratio stems from rendering said distribution of pixels on a screen with 4 3 proportions, typical of monitors at the time. Text modes 4. Extended graphics modes 1. Artifact colors using a NTSC monitor 1. IBM intended that CGA be compatible with a home television set. The 4. 02. 5 text and 3. Cga p. 0. png CGA 3. Cga p. 1. png CGA 3. Cga p. 3. png CGA 3. CGA program interface. PCPaint in 3. 202. Note the use of dithering to overcome the CGA palette limitations. CGA 6. 40x. 20. 0 game. Sim. City in 6. 402. Note the use of dithering to simulate gray tones and non square pixel ratio that deforms the fonts. Color paletteeditDespite varying bit depths among the CGA graphics modes see below, CGA processes colors in its palette in four bits, yielding 2. The four color bits are arranged according to the RGBI color model the lower three bits represent red, green, and blue color components a fourth intensifier bit, when set, increases the brightness of all three color components red, green, and blue. Employee Compensation Act 1923 Bare Act Pdf. In graphics modes, colors are set per pixel in text modes, colors are set per character, with an independent foreground and background color for each character. Full CGA 1. 6 color palette. AA9light blue5. 55. FF2green0. 0AA0. FF5. AAAA1. FFFF4redAA0. FF5. 55. 55magentaAA0. AA1. 3light magentaFF5. FF6brownAA5. 50. FFFF5. AAAAAA1. FFFFFFWith an RGBI monitoreditThese four bits are passed on unmodified to the DE 9 connector at the back of the card, leaving all color processing to the RGBI monitor connected to it. With respect to the RGBI color model described above, the monitor would use approximately the following formula to process the digital four bit color number to analog voltages ranging from 0. Number 44 13color. Number 88. Number 22 13color. Number 88. Number 11 13color. Number 88. Color 6 is treated differently when using the formula above, color 6 would become dark yellow, as seen to the left, but in order to achieve a more pleasing brown tone, special circuitry in most RGBI monitors, including the IBM 5. Number 6 thengreen green 2. It is this RGBI with tweaked brown palette, shown in the complete palette to the right, that all later PC graphics standards such as EGA and VGA have retained for compatibility as a power on default setting of their internal palette registers andor DAC registers. With a composite color monitortelevision seteditFor the composite output, these four bit color numbers are encoded by the CGAs onboard hardware into an NTSC compatible signal fed to the cards RCA output jack. For cost reasons, this is not done using an RGB to YIQ converter as called for by the NTSC standard, but by a series of flip flops and delay lines. Consequently, the hues seen are lacking in purity notably, both cyan and yellow have a greenish tint, and color 6 again looks dark yellow instead of brown. The relative luminances of the colors produced by the composite color generating circuit differ between CGA revisions they are identical for colors 1 6 and 9 1. CGAs produced until 1. CGAs due to the addition of additional resistors. CGAs 1. 6 colors when using the NTSC output post 1. RGBI monitor availabilityeditWhen the CGA was introduced in 1. IBM did not offer an RGBI monitor. Instead, customers were supposed to use the RCA output with an RF modulator that they obtained separately, from a third party to connect the CGA to their television set. The IBM 5. 15. 3 Personal Computer Color Display would not be introduced until March 1. Resulting from the lack of available RGBI monitors in 1. RGB monitors without provisions for the intensifier bit, reducing the number of available colors to eight, and displaying both colors 6 and 1. This is relevant insofar as if an application or game programmer used either one of these configurations, they will have expected color 6 to look dark yellow instead of brown. Standard text modeseditCGA offers four BIOS text modes called alphanumeric modes in IBMs documentation 4. Each character is a pattern of 88 dots. The effective screen resolution in this mode is 3. The choice of patterns for any location is thus limited to one of the 2. ROM chip on the card itself. The display font in text mode the hardware code page. IBM CGA, it is possible to select one of two different fontsnormal or thinby changing a jumper. Many clones didnt offer this possibility. The card has sufficient video RAM for eight different text pages in this mode. BIOS Modes 0 1 select 4. The difference between these two modes can only be seen on a composite monitor mode 0 disables the color burst, making colors appear in grayscale. Mode 1 enables the color burst, allowing for color. Mode 0 and Mode 1 are functionally identical on RGB monitors and on later adapters that emulate CGA without supporting composite color output. Each character is again an 88 dot pattern the same character set is used as for 4. The effective screen resolution of this mode is 6. Again, the pixels cannot be individually addressed. Since there are twice as many characters on the screen in this mode, the card has enough video RAM for just four different text pages. BIOS Modes 2 3 select 8. As with the 4. 0 column text modes, Mode 2 disables the color burst in the composite signal and Mode 3 enables it. In every text mode, each character has a background and a foreground colore. While the same 4 bit nybble value used for the foreground color would normally allow all 1. CGA independent of the CPU.